How does waste management work: why it is Important
Waste is merely a raw material in the wrong place
This Topic Cover:
Why Solid waste management is essential for urban centres ?
Caveats of present waste management process.
Solid waste management techniques.
Use of compost making Machine.
Large scale facilities that employ composting techniques.
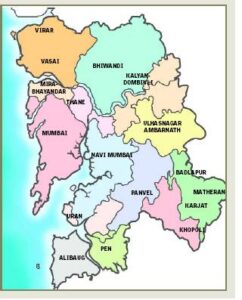
Mumbai metropolitan region is has an area that consists of the state capital of Maharashtra which is Mumbai and its satellite towns. The region has an area of 4355 km square and is one of the most populated regions in the world. Mumbai district has an area of 157 km square. Mumbai being a financial hub of the country attracts investment as well as various business resulting in an influx of people for employment purposes. Inspite of small area Mumbai has a population of 12,442,373 (2011 census figures) and the population of total Mumbai metropolitan region is 18,394,182 (2011 census figures). The following Map shows the extent of Mumbai Metropolitan region.
The below table shows whether or not a municipal corporation in Mumbai Metropolitan area has a separate department concerning to solid waste management or not.
Similarly the below table displays whether the municipal Council has a department dedicated to solid waste management or not.
Thus we can see which of the following Municipal corporations and Municipal councils have a Solid waste management department. Various Municipal council and municipal corporations that do not have a separate department of Solid waste Management put the responsibility of waste management under Public work department or Public health department.
However the MMRDA or the Mumbai metropolitan region development authority has already a department dedicated to SWM and plans for a new waste management facility are already undertaken at Taloja (Near Kharghar) which is projected to dispose 1800 metric ton waste for the next 25 years per day.
Why Solid waste management is essential for urban centres ?
While we can debate about the pros and con of having a separate department concerning the solid waste management it is highly essential we understand the need of waste management at all.
-
Mumbai has already a high population of 12,442,373* (Mumbai census 2011) and it is estimated to grow in the next 3 decades to 42,400,000 approx in 2050. Such high levels of population will eventually create huge waste generation. Currently with 2011 population levels the per capita waste generation is 0.63 kg. Mumbai is generating 7800 MT waste every day.
-
The current per capita waste generation is estimated to rise to 0.7 kg per person in the year 2025.
Let us also compare the waste generation of Mumbai compared with other regions nearby.
It should also be noted that of of the total waste generated it is estimated that about 45% of the waste generated is biodegradable and the rest is non biodegradable.
Current management structure
Waste management responsibility is taken formally by the MCGM. The current mechanism involves collection , transport and disposal strategy. Waste is collected from different areas in Mumbai and sent to disposal at 3 dumping ground (Deonar, Mulund and Gorai )sites which are currently services the city and are already overburdened with waste. The following mechanism explains the present structure.
The garbage collectors employed by various housing societies, entities etc. collect the garbage on door to door basis and dump it near the community bins strategically placed at various areas. There are more than 5800 community bins in Mumbai alone. Here manual or mechanical compactors are used to collect waste from such community bins and and then sent to a transfer station. In case of Mumbai the transfer stations are located at Mahalaxmi, Kurla and Versova. The transfer stations are basically stations for smaller vehicles that bring the garbage from point sources and community bins. The garbage is thus transferred from smaller vehicles to larger vehicles capable of transferring the waste towards the disposal sites.
Various types of vehicles are used to transport the garbage. Those include open flat-bed trucks, covered trucks, mobile compactors, tarpaulin covered vehicles .
Tarpaulin garbage (construction debris carrier)
A garbage truck (closed bed )
In Mumbai
About 95% of waste generated in the city is disposed in such manner.
Caveats of present waste management process.
Dumping grounds
The current dumping grounds in Mumbai are in Deonar, Mulund and Gorai. The combined area of the 3 landfills is 140 hectares. Area of Mumbai in comparison is 60340 hectares. Thus landfills constitute only 0.22% of the total area of Mumbai. The term landfilling refers to the practice where waste is being disposed and stored under more or less controlled conditions. Principles of landfilling include compaction, leveling of waste and final covering by earth, leachate collection system and landfill gas extraction. However due to space constraints and opposition from various citizens to create landfills spaces makes this option a far less viable option in the future.
Concerns regarding landfills
-
Effects biodiversity as species that thrive on refuse (rats, crows etc.) compete with other local species thus endangering them.
-
Leachate production.
-
Health impacts for nearby residing residents.(landfills operate as mosquitoes breeding grounds)
-
Unpleasant visual effects due to the sites ruining natural landscape and the protest of citizens towards landfills as they cause problem of vermin, spread of diseases and also lower property prices.
Debris Disposal
Mumbai generates about 2000 tons of construction debris. As transportation of such debris is deemed to be expensive towards the dumping sites, various construction activities in Mumbai that generate waste will use loopholes and illegal ways to dump the construction debris. Due to lack of space in Mumbai the waste has to be carried off towards long distances. This increases the transportation cost leading to the business becoming ‘unprofitable’. Thus such debris is dumped into the creeks which affects the ecosystem of mangroves. The ecosystem of creeks in regions of Vasai, Gorai, Mankhurd are already endangered due to illegal dumping of waste.
Open burning, landfill fires resulting in deterioration of air quality-
On January 27th 2016 Mumbai witnessed a smog generated due to a mysterious fire that started in the deonar dumping grounds. The fire was huge enough to cause a smog in the city for 3 days and was visible by satellites in outer space. Regions in Mumbai had seen huge levels of pollution levels with the air quality index reaching 347 which comes into hazardous category seriously affecting health of citizens in Mumbai. As a result schools were closed for 2 days with citizens advised to remain at homes.
There is also the problem of open waste burning in various parts of India. Open waste burning primarily occurs due to the following reasons.
-
Open burning by rag pickers to isolate metals from waste.
-
Open burning by residents and and municipal workers to reduce MSW.
-
Open burning by homeless people for warmth generation at night.
While NGT has imposed a ban on open burning of waste with a fine upto 25000 rupees. The law is generally not implemented.
A 2010 study by NEERI in Mumbai conducted about air quality assessment has stated about 2% of total MSW waste generated is burnt on the streets and about 10 % of the waste is burnt in landfills.
MSW burning results in largest contribution towards Carbon Monoxide and PM (particulate matter ).
Sourced from cpcb.nic.in
Thus as explained in the above pie chart open burning is the 3rd largest contributor towards CO pollution in Mumbai.
Deonar burning as witnessed from satellites.
Water pollution-
In landfills biological degradation of waste results in generation of leachate. Such leachate can pollute the water sources nearby the landfill areas and may also pollute the groundwater.
Leachates are generally formed due to anaerobic decomposition of biodegradable waste which is often mixed with heavy metals (such as chromium, lead, nickel )developed from inorganic waste. Such metals increase the solubility of iron and manganese in groundwater thus increasing the concentration resulting in increased groundwater pollution.
Impact on Climate change
Climate change caused due to anthropogenic activities is one of the biggest problems the world has to face. Due to waste storage at landfills in particular, there are incidences of methane releases. Such methane released due to solid waste management operations should be captured. Thus organic waste which is decomposed at landfills have the problem of anaerobic decomposition leading to formation of methane gas. Thus to prevent methane formation it is essential to avoid an-aerobic decomposition.
Solid waste management techniques.
The following are the ways by which the problem of Solid waste management are currently been studied and even implemented.
Waste to Energy (WTE)
Refers to method of generating energy in the form of electricity and/or heat from waste, usually through combustion. The combusted waste generates steam which could be utilised to drive a steam turbine thus resulting in energy generation. It also avoids the problem of leachate seeping underground thus reducing groundwater contamination. But while the method seems great at first glance it also has its own caveats. First and foremost waste to energy needs huge quantities of waste generated and later to be incinerated resulting in a possibility to divert resources from recycling plants. Also high amount of wet waste generation also results in difficulty in burning the waste.
Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)
A fuel produced by shredding and dehydrating combustible MSW. RDF can be used for industrial purposes instead of coal. RDF are pellets created from trash which can act as a viable alternative for burning purposes. Input materials needed for RDF consists of waste that have a high caloric value.
E.g- paper industry rejects, Plastic packaging, High caloric plastics, Mixed waste from household, industry.
Concerns regarding Refuse derived fuel
-
The cost effectiveness of the process to generate electricity.
-
Toxic and polluting gases emitted by such fuel generation and use.
-
Also the problem of using mostly dry waste for power generation which again could be used for recycling purposes. Wet waste mostly needs to be segregated from RDF plants. So it basically solves only a part of problem.
Currently BMC has floated tenders for deonar dumping ground for a setup of a waste to energy plant. But due to lack of segregation deonar dumping grounds which can cause reduced calorific value of the combustible waste (due to mixture of wet organic waste) there are not many parties interested to take up the challenge citing, economic feasibility of the project.
Recycling
Recycling is perhaps the best sustainable long term solution for the waste management issues. The inorganic waste collected can be considered as a fodder for recycling.
Plastic, metal, Paper, E waste are easily recyclable and can be reused further. However Recycling is mostly undertaken by formal sector.
Generally speaking, Plastic, glass and metal is exchanged with kabadiwalas at household levels. The kabadiwalas act as a intermediate between waste processing centres. The rest of plastic and metal collected come from a array of informal workers called as ragpickers which also include children as well. Mumbai is home to one the biggest slums in the world called Dharavi slums which surprisingly works as an industrial recycling unit as well. Dharavi’s 13th compound an area which is associated with recycling since decades. It currently employs more than 5000 people in the recycling industry. The area acts as a big segregation plant with collection of plastic, plastic drums, iron scrap, cotton scrap, empty bottles, glass etc.
Composting
Composting signifies biological decomposition of organic material. Microorganisms decompose the organic material to a stabilized product, i.e. compost. The end product can be used as soil conditioner. The compost generated consists of useful bacteria which can help plants with numerous benefits such as nitrogen fixation, helps soil for water retention, adds nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Thus benefits of compost are numerous and unlike the above alternatives this method seems viable and sustainable in the long run. It is also in sync with nature in general. Composting has the following benefits to agriculture and environment.
Environment
-
Directs waste away from landfills resulting in less accumulation of garbage and reduces leachate production (which could contaminate underground resources )
-
Reduces foul odours
-
Avoids methane production in landfills
-
Helps in afforestation programmes and increases the survivability of plants.
-
Reduces need for landfill space*
Agriculture
-
Helps maintain soil ph levels
-
Adds water retention capacity of the soil
-
Adds organic matter, humus which supplements the soil.
-
Reduces fertiliser requirement
-
Provides a market for compost making and selling thus creating an extra income for the farmers
-
Compost attracts earthworms thus helping in better soil aeration.
-
Helps restore soil conditions as microbes are affected with high usage of chemical fertilisers.
Composting seems a feasible way to solve some of the problems associated with waste management. The BMC has given a deadline on 2nd of october 2017 regarding waste management. The circular stated that entities that generate more than 100kg of wet- waste every day should install within their own capacities to dispose the wet waste. Therefore a lot of entities have made various attempts to segregate the wet waste generated at source from the inorganic waste and utilised the wet waste generated for composting processes. The following techniqies have been utilised by them.
USE OF COMPOST MAKING MACHINES
Various shopping malls, industrial setups, offices have been using a in-vessel waste composting machine which is basically a mechanical machine that works using electricity, manual labour to convert the wet waste generated into useable compost. The following image shows the machine which is used.
* A typical in vessel composting machine based on electric power.
Such machines have capacities ranging from low as 5 kg per day to 500 kg per day of wet waste to compost. These machines are the fastest when it comes to create compost. It usually converts the waste into usable soil additives within a 24 hour time. However the major drawback of the machine is the requirement of electric power which adds to the cost and also the initial capital investment needed to purchase these machine.
Such machines are now being installed at various places in Mumbai from where BMC does not collect waste.
Another machine that solves the issue of wet waste is an in vessel biogas waste generator.
See image.
Here the operation is simple, the wet waste generated is put into the plastic tanks and with enough time to generate an-aerobic process slurry and biogas can be collected to generate useful energy. Biogas generated from such processes can be utilised as a gas to produce heat necessary for cooking purposes. However the biogas production takes time to generate and also the machine is bulky which would take up space for large amount of food waste disposal.
Manual composting machines.
This types of machines are simple in construction which is basically a rotary device which can be rotated manually with the help of a handle. The idea is to store wet waste in such containers and usable compost will be created naturally in a span of 15-20 days. The machine needs to be rotated in order to ensure better mixing and aeration of the waste. However the process though is less costly takes time to create compost and might not be feasible with large generation of food and wet waste. Also will require ample space. See image.
* a typical rotary bin composter. There is also an image of shredder which shreds large wet waste particles into smaller particles for faster composting.
Vermicomposting and Composting pits
Various methods that incorporate wet waste composting through the use of earthworms have also been undertaken. The worms eat away the wet waste and produce usable compost. An suitable environment is provided for vermicomposting to take place. However such composting processes take huge amount of land and time consumption as well.
*vermicomposting pile of wet waste.
Such type of composting is produced by entities which have ample space or property to use such techniques.
Large scale facilities that employ composting techniques.
Mechanical biological Treatment plants (MBT ) were installed as early as in 1970’s. They however were not popular due to high amount of imported technologies used and thus running into financial hurdles. Also there was lack of market for the compost generated and process was getting affected during rainfall. Also the mixed nature of waste resulting in metal and hard particles affecting and damaging the machinery at regular intervals. The process involves shredding of wet waste into smaller particles, which would then be dried, shredded and then turned into compost and finally stored for the ‘curing’ process a process where compost temperature is stabilised after a particular time duration ranging from 1 to 3 months depending on the weather.
*a plant for compost preparations.
Navi Mumbai currently has a MBT plant in operation that takes in 300MT of waste per day. Wet waste is segregated using belt drivers and blowers/ Magnets and finally using manual labour for segregation.
Concerns regarding compost
-
While this seems to be a very viable option in regards wet waste management. It does not address the problem fully as inorganic waste cannot be composted.
-
Composting requires pits which use a large area. This creates problems in urban areas where space is already a constraint.
-
Compost is bulky and expensive to transport.
-
Rate of nutrient release is slow as compared to chemical fertilisers. Therefore not viable for short term benefits of plants. A good solution will require the use of both (chemical fertilisers and organic compost)
-
Agriculture users might have concerns regarding municipal waste as compost due to fear of heavy metals present in compost .Especially in regard with food crops. The fear that unprepared compost could affect crop production needs to be addressed.
-
Subsidies on chemical fertilisers make compost less lucrative as chemical fertilisers are already tried and tested therefore farmers will be skeptical to change.
Other Initiatives –
Advanced Locality Management-
Advanced Locality Management (ALM) is local managem
ent of solid waste by citizens who organise themselves to manage their waste. Wet waste is segregated at the source and dry waste is then exchanged with scrap dealers or then disposed off with the collaboration with rag pickers. There are in all 719 ALMs along with 276 vermi-compost pits spread over the city. This way, approximately 20-25 tonnes of garbage per day is prevented from reaching the dump yards. Another encouraging fact is that women run 80% of these ALMs. The goal is to ensure maximum citizen participation . Organisation of
the community, training and initiation is done with the collaboration between residents and MCGM.
Summary
The government should work in hand with BMC and other urban local bodies along with NGOs to tackle the problem of solid waste management in the city. The current changes in BMC circular of 2nd october has spawned a lot of entrepreneurial interest to solve the challenge of solid waste management. Also the government must focus initiatives on source separation, recycling of waste, production and utilization of high quality compost. The government should also educate and inform the citizens the goal of solid waste management and urge local governments to form a department catering to the needs of solid waste management. But the panacea to the issues facing the solid waste management plan lies in making sure waste is segregated at the source. Blue green pledge will ensure the sustainability of urban centre in the long run.
The benefits in finding a sustainable path to solid waste management has multiple advantages. It will impact the quality of life, help battle climate change, generate economic growth, bring informal character associated with the industry to a formal character. It is then and only then the below quote will began to make much more sense.
‘Waste is merely a raw material in the wrong place’