A Sustainable Solution on Organic Waste Management Methods
So… Trash! Not exactly dinner table talk, right? But, let’s face it – it’s 2024, & waste isn’t a problem anymore! But, an opportunity for us to live in a world where, “Sustainability” – isn’t just a big word!
Wanna know more about what waste management is? & how it’s getting a tech upgrade??
Let’s roll up our sleeves, put on some gloves & start digging – it’s time to get our hands dirty in the Waste Game…. Because this trash isn’t going to manage itself!
Now, we all know our world is upgrading at a light speed! And with growing cities, industries, & infrastructure; Man is creating trash at an alarming rate and to be honest, it ain’t pretty…
And now, due to continuously overflowing landfills, people are getting sick left and right… That’s not it – it is also greatly affecting all the nature by causing depletion of resources & endangering the earth’s ecosystem in the process!
Now you might be wondering, “What it has anything to do with me?” The thing is you are a small but inseparable part of the picture which is forming around and by having an awareness about the envirnoment might just increase your chances of living a Sustainable Future!
Let’s start with the basics… What exactly is Waste Management?

To put is simply… I’d say, “Collecting, sorting, processing and disposing of trash!” There are many things involving the concept of waste management, but … I’m gonna keep it simple so that everyone could wrap their heads around it, and like talk about – Composting!
I mean… compared to Incineration, Composting is way more commonly known term! Speaking of which, if you want to get rid of the organic waste produced in your households daily then, Composting is for you!
Because you can easily convert this waste generated at home into a nutrient-rich compost which improves soil quality of that one potted rose plant hanging on your balcony or your mini vegetable garden in the backyard! And it also promotes sustainable agriculture methods… What more you can ask for? huh…?
To be honest, there are a bunch of techniques for composting too! One of which is recommended by the people at Klimrus Sustainable Solutions Pvt. Ltd. is their “Solar Composting Machine Set” which is an all-in-one solution to your problems… It is one of the most innovative ways to hasten the composting process… And it is totally eco-friendly as it runs on solar power and no electricity is consumed!
Now… I know what you are wondering… “OUT WITH IT!” Tell us everything you know about it, right?!
But let’s not rush it… I’m gonna share all the infomation that you need to know one-by-one whether its about waste management as a concept, organic waste management by converting it into compost, and/or about the Klimrus Solar Composting Set; that not only solves all your problems but, is also totally eco-friendly as it works on solar power!
As I mentioned before, Waste Management is bascially collecting, sorting, processing and disposing of trash… So, now that you know the basics let’s dive a little deeper…
We can start by mininmizing the trash and instead of processing waste find new ways to reuse it (the things that could be reused). By converting trash into fresh goods by recycle the dry waste. We can also, convert garbage into energy by burning it to generate power or we could just convert it into compost as a totally eco-friendly means of disposing wet & organic waste…
Now, to dive in a little further, let’s see how waste management & composting are related to each other at a root level! Shall we?
So…. for all the organic waste generate at home such as, leftover food, expired food, dairy products, yard trash, etc. can be easily tranformed into a nutrient-rich compost as microorganisms present in this waste helps it to decompose and break-down the garbage which after complete decomposition converts into compost!
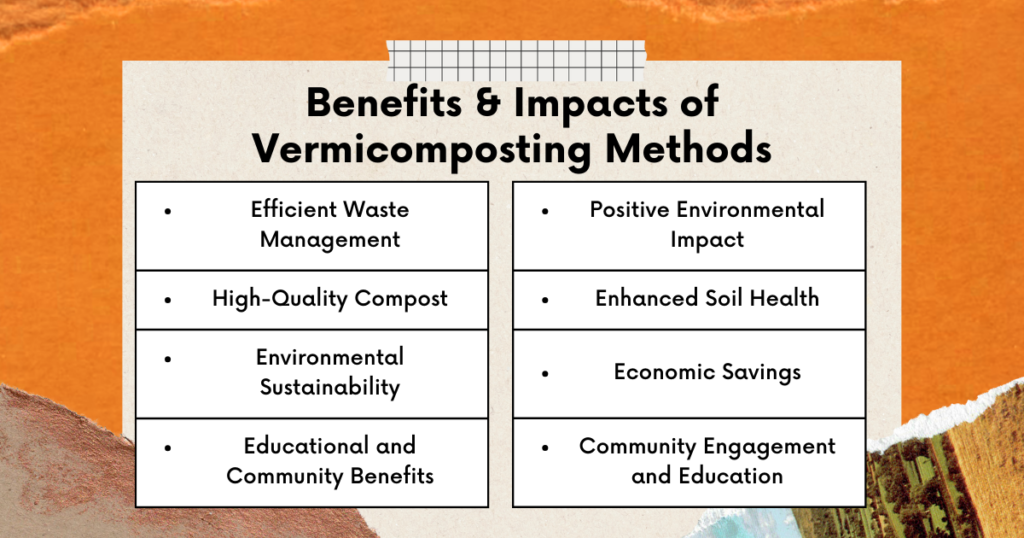
Here are a few composting methods which I am too lazy to explain so instead I’m showing you image which is way easier to understand… why? Beacuse, A picture speaks a thousand words & I’m hoping this one too!

And in case you wish to know more about these methods… Click Here!
That’s not it, the compost generated by this waste can be served as a valuable commodity which enhances the soil, prevents erosions & promotes in sustainable agriculture; it also keeps organic waste out of landfills, assisting in the reduction of dangerous gasses like methane!
Just like a coin has 2 sides even waste management has it’s fair share of advantages & Disadvantages… But, since I’ve already mentioned that i’m feeling lazy I’m gonna brush over through the image given below… Don’t worry, it’ll briefy give you the idea about the good & bad sides of Waste Management without boring you in the process! And if you still wish to know more about it, Click Here!

Now, I’ll just jump straight into the world created by the people at Klimrus Sustainable Solution! Let’s see, what cutting-edge technologies they have in store for us which would help us create compost using solar-powered composting techiques!
As I mentioned before, Klimrus Sustainable Solution Pvt. Ltd has discover a eco-friendly approch towards composting by using Solar-powered Composting Machine set which makes it perfect product for building/Housing Societies, vast gardens, farms, town, & institutions who are searching for environment friendly ways to manage their trash!
Okay… We’ll go ahead step-by-step starting with what are these machines?, what’s the process that take place in each machines?, and what are the things that you need to do? and advantages of using these machines?
Let’s start with the First one question – What are these Machines?
There are three main parts of this system consisting of a shreddeing machine, a solar composting & cooling carts.
Now … I know it sounds really boring because it is… But I’ll still try to keep it simple so that at least it’ll finish faster… right?!
So.. the first up is “The Shredder Machine” This machine primary work is to break down the organic material into smaller pieces. Some benefits of this machine are:
- Speeding up the composting process by breaking things down into smaller particles.
- Prevents the trash from rotting as a big pile cause that’s hard to handle.
- Ensure that the consistency of breaking down of materials..

If want to know more what are the organic materials and how it works you can check our blog Manual Shredder though it’s a different model but the function is same! Click Here!
Next up is ” The Solar Composting Machine” This machine is called the heart of the process by the people at Klimrus, not me! Anyways… the main objective of this machine is to create & maintain an ideal environment for microorganisms to break down the trash into small pieces. As you can guess, this machine does a lot stuff and it can be hard to understand if start explaining it but, to put it simply the process of decomposition take place inside this machine using it’s various feature which I’ll explain in easiest way possible …
Here’s what goes around in this machine:

First of all, to enhance the process of decaying of the waste we put inside after shreddeing it into smaller particles, we need to maintain the temperature between 55°C – 65°C… which sounds like a pain but, don’t worry the machine does that for us! So… we could brew tea in the mean time! Haha… I mean jokes apart… Due the solar panels, the machine keeps genrating the required amount of heat without us losing any sweat!
And now you might be wondering why we have to maintain temperature and stuff? I won’t bore with the details but, to put it simply it speed up the microbial activity (decaying) of the waste!
Now… moving on to the next thing that happens inside of the machine, I know you’ll be like if we just have to put the trash in the machine and wait why do we even need to know what’s going inside it, right?!
to be honest… I get your point but knowing a few things won’t hurt anyone and I’m telling you this because I’m an employee and can’t argue with my boss … so, for the sake of all of us.. I try to keep it simple enough for you to grasp & hopefully I’ll get by saying I wrote a blog as you wanted me to, & be done with it!!!
And What were we talking about? Ohh yeah… the next part of the process… so, after the machine maintains it proper temperature, a built -in aeration devices keeps the pile of waste inside it oxygenated… It means aiming already existing oxygen in the air to the pile of waste inside the containers with the help of these blower fans, so that it would continues to speed the decomposition process at a faster speed & avoid producing any foul smells… !
The last thing that goes on inside this same machine is Moisture control! Basically, this machine is designed also, maintain right moisture levels for the little germs to do there thing! So that, any unneccessary excess mositure is absorbed & it won’t get too dry either.. just a right amount of moisture needed for decoposition!
Now the thrid product included in this Solar composting system are Cooling Crates! After everything is done… I mean the process inside that solar composting machine, we just need to transfer this hot compost into these carts provided in the set… Now, just let it cool for a day or two and you are ready to use the natural nutrient-rich compost for gardens or yards or even agriculture; choose your pick!

If there are still any answered questions I’ll lay it down the things that you have to do while handling these machines and what’s your role in this whole process…. right?
-
Step 1
You need to collect all the organic/wet waste which usually means things like kitchen scraps,dairy products, uncooked food, fruit & vegetable peels, meat or fish remains & small bones, expired food items, dry leaves, small branches, etc! I hope you got the gist of it, right?
-
Step 2
Put everything you’ve gathered inside the shredder machine, this is an automatic shredder machine so, you just need to put stuff in, click the buttons and wait for it to shred the waste into smaller particles and later collect it from the outlet at the bottom.
-
Step 3
Now, put the shredded wet waste into the Solar composting machine containers… At this point you need to do one more thing; you have to put sawdust provided with the Solar Composting Machine Set! I know… more questions coming at my way… so, I’ll answer them before you ask me!
Sawdust is a bulking agent that after adding to the mixture helps to absorbs any exccess moisture generated due to heating & it also balances carbon-to-nitrogen ratio which extermely important for composting! Also, one important thing before I forget… You have to keep adding waste daily for 10-12 days and behind each batch of waste you add, from day 1 to day 10th/12th, you should add 10% sawdust of the total amount of waste to added each time; (e.g. 1 Kg Waste = 10% of 1Kg, which is 100 g – Sawdust!) I know maths of it could be tricky but so I did it for you in the chart given below!
-
Step 4
Now, you just sit back & relax as the solar composting machine takes over th charge of converting the waste into compost! And since I alreading explained it eariler what exactly it does… I won’t rumble about the same stuff over & over again!
-
Step 5
Okay so, you have to follow the step 3 of putting daily waste in the solar composting machine for 10-12 days with the right amonut of sawdust that I’ve mentioned!
-
Step 6:
After the composting process is complete, just transfer the hot compost into the cooling crates and wait for a day or two; then they are ready to use!
-
Step 7:
Use it as you please whether it’s for personal or commercial use, it is totally dependent on your choice! I can’t write any more steps… cause there aren’t anymore left… !!! Thankfully!!!
(Note: Don’t put plastic or any non-degradable things in it, make sure that you only put organic waste in the shredder & the solar composting machine!!!)
So… Now in conclusion I have nothing to say because the this Solar composting machine set speaks for itself! and to be honest I’ve been writing this particular blog for like a week now! Yeah I too tired and frankly a little frustrated cause I couldn’t think of any other way to explain about this solar composting system anymore! I’ve added links that would clear any remainig that you may have about this composting system. and for more details you could visit out YouTube Channel: Click Here!
Written & Edited by ~



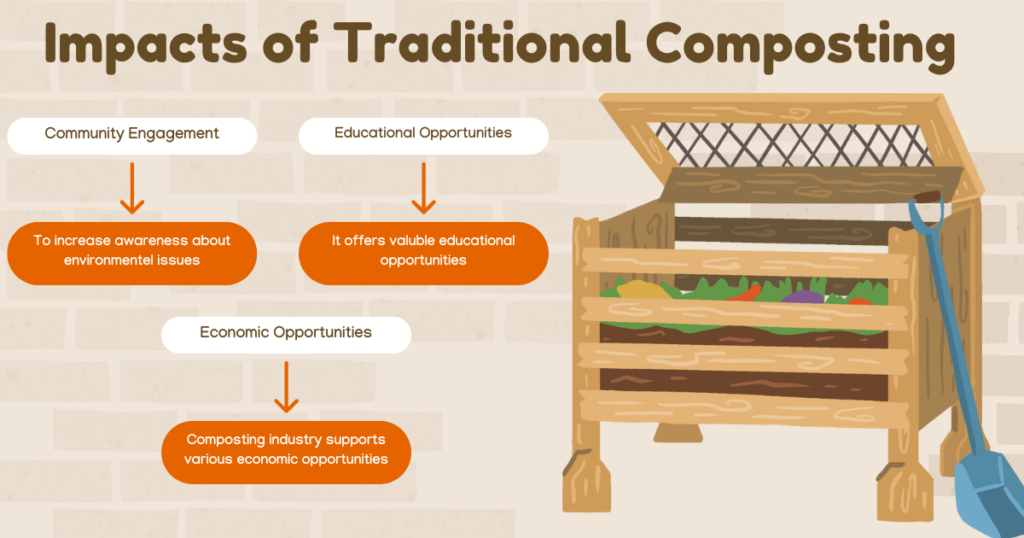





 Read more: Traditional Composting Methods…
Read more: Traditional Composting Methods…