By Harnessing Solar Compost Machines convert Organic Waste into Rich Compost
By harnessing the energy of Solar Compost Machines is one such invention that is causing a stir towards traditional home composting techinques. This method effectively turns organic waste into compost by utilizing renewable energy, which has the added benefits of reducing waste and improving soil. Implementing creative and environmentally friendly techniques has become crucial in today’s society, when environmental sustainability is more than just a catchphrase. We’ll analyze the internal functions of sustainable solar compost machines in this in-depth instruction, as well as their many advantages and useful home composting advice, enabling you to convert garden waste and leftover food into nutrient-rich compost.
Understanding the Solar Compost Machines
Utilizing solar energy to speed up the decomposition process, solar compost machines are an innovative spin on traditional home composting techniques. These devices usually consist of a few basic parts:
Solar panels: These panels, which are mounted on or next to the machine, collect sunlight and transform it into electrical energy. The machine’s internal mechanisms are then powered by this energy.
Composting Unit: The organic waste is contained in the chamber, which also offers a controlled decomposition environment. It often includes characteristics like temperature control, moisture management, and customizable aeration.
Aeration System: The aerobic breakdown process depends on optimal oxygen levels. The composting chamber’s air circulation is maintained by the aeration system, which promotes the development and activity of helpful microorganisms.
Mixing Mechanism: A machine that is used in certain solar compost machines to periodically mix the materials. This speeds up the composting process and keeps the pile from compacting by helping to spread heat and moisture more evenly.
Control System: Digital controls which let users monitor and regulate the temperature, level of moisture, and aeration levels are a common feature of modern machines. Furthermore, some advanced electronics allow for remote monitoring using smartphone apps.
The eco-friendliness and effectiveness of solar compost machines are what make them wonderful. Because they use solar energy, they are a great option for eco-aware homes and communities because they minimize the dependency on electricity from non-renewable sources.
Benefits of Solar Compost Machines
Solar compost machines offer a range of benefits that go beyond traditional composting methods. The advantages of solar compost machines detail:
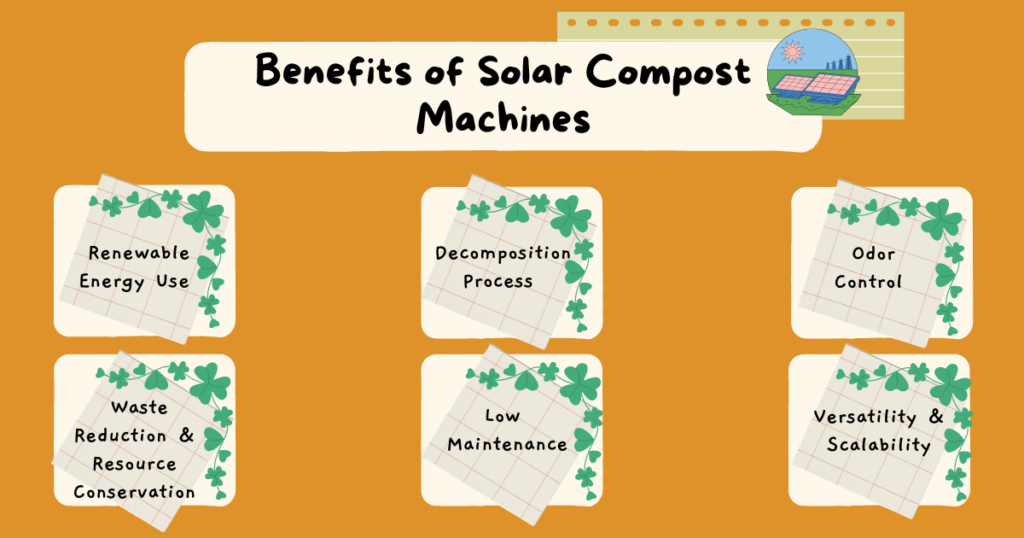
1. Renewable Energy Use
Considering that solar compost machines depend on renewable energy is one of their biggest advantages. Utilizing solar electricity can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions because it is an endless, clean supply. They operate by using solar energy instead of fossil fuel-derived electricity, which makes them an environmentally friendly choice for solar composting. This encourages a greener lifestyle in addition to reducing the carbon footprint of your waste management procedures.
2. Decomposition Process
The optimal circumstances for decomposition are provided by the regulated environment found within a solar compost machine. The device creates the optimal environment for rotting bacteria by keeping the temperature and moisture levels just right. As a result, organic waste decomposes more quickly than conventional compost heaps. Due to its efficiency, compost can be produced more quickly, giving you a steady supply of rich, healthy soil for your landscaping or gardening needs.
3. Odor Control
A significant concern with composting is the possibility of unpleasant smells, particularly in areas with dense populations. Solar compost machines are made to reduce this problem to the minimum. By supplying oxygen continuously, the aeration system avoids anaerobic conditions, which can result in foul odors. The regulated atmosphere further reduces the possibility of luring pests. Because of this, sustainable solar compost machines can be used in a variety of places, such as community gardens, homes, and schools.
4. Waste Reduction & Resource Conservation
Organic waste can be kept out of landfills, where it would otherwise contribute to the production of methane, a powerful contributor to global warming, by composting it. In addition to minimizing the amount of garbage dumped in landfills, solar composting replenishes the soil with beneficial nutrients. By enriching the soil, this technique raises its fertility and structural quality. This could lead to a decrease in the demand for chemical fertilizers, encouraging a more organic and long-term method of farming and gardening.
5. Low Maintenance
Solar compost machines accelerate the process, whereas traditional composting systems involve frequent rotation and observation. They require very little maintenance once set up. You no longer have to stir the compost pile by hand because the automated systems take care of the aeration, mixing, and temperature management. Because of its ease of use, solar compost machines are a great option for families and busy individuals who want to adopt sustainable habits into their everyday life without having to spend a lot of time on them.
6. Versatility and Scalability
Solar compost machines can be customized according to various kinds of locations and requirements due to their diverse sizes and designs. You can locate a machine that meets your needs whether you have a huge rural property or just a small urban garden. These devices can also process a variety of organic materials, including agricultural wastes and yard waste in addition to kitchen scraps. Because of its adaptability, a variety of materials can be composted, which raises the caliber of the finished compost even more.
Practical Tips for Traditional Home Composting Methods
Traditional home composting techniques are still a useful and accessible choice, even though solar composting machines provide a cutting-edge and effective approach to handle organic waste. If you follow a few simple rules, traditional home composting at home may be profitable and easy. Here are some helpful guidelines to get you going and ensure success:

1. Choosing the Right Location:
For traditional home composting to be successful, the location of your compost pile or container is essential. Choose a well-drained location to avoid waterlogging, which can result in anaerobic conditions and odors. The breakdown process is accelerated up by a warm temperature, which is maintained in a sunny spot. For best energy generation, make sure the solar panels on your solar compost machines receive enough direct sunlight throughout the day if you’re using it.
2. Balancing Green & Brown Materials:
Green and brown materials must be mixed in a balanced way for a compost pile to be successful. Green materials, which include things like coffee grounds, vegetable scraps, fruit peels, and grass clippings, are high in nitrogen. Newspapers, cardboard, straw, and dried leaves are examples of brown materials, which are high in carbon. Maintaining a ratio of approximately two parts brown materials to one part green materials is a basic rule of thumb. A healthy carbon-to-nitrogen ratio is ensured by that balance, which is essential for effective decomposition in the traditinal home composting.
3. Maintaining Moisture Levels:
An essential component of the traditional home composting process is moisture. Like a sponge that has been wrung out, the compost pile should be damp. The rate of decomposition will slow down if it gets too dry. If it’s overly damp, anaerobic conditions may develop, which can cause smells and a slower rate of disintegration. Check the moisture content of your compost pile frequently, and add dry materials or water as necessary. For instance during wet or dry seasons, covering the compost pile with a tarp or top can assist maintain steady moisture levels.
4. Turning the Pile Regularly:
Aerobic decomposition requires aeration. Turning the compost pile on a regular basis promotes the addition of oxygen, which stimulates the development of advantageous bacteria. Additionally, it keeps the pile from compacting and permits moisture and heat to be distributed evenly. Every few weeks, stir the contents of traditional home composting piles using a garden fork or compost turner. The integrated mixing mechanism in solar compost machines may take care of this chore automatically, saving you valuable time.
5. Monitoring Temperature:
A useful measure of the composting process is temperature. A thoroughly cared-for compost pile will warm up, sometimes reaching temperatures of 130°F to 160°F. The organic matter is broken down by microbial action, which generates this heat. You can assess the progress of your compost and make any adjustments, like turning the pile or adding extra green materials, by keeping a regular eye on the temperature. A compost thermometer can be a helpful tool for traditional compost piles, and solar compost machines frequently include temperature monitoring built in.
6. Avoiding Problematic Items:
Not every organic item can be composted. Meat, dairy products, fats, oils, and bones should not be added to your traditional home composting piles since they might draw bugs and produce bad aromas. Furthermore, keep in mind that composting damaged plants or weeds with seeds may not completely destroy diseases or weed seeds. For optimal effects, stay with plant-based materials, eggshells, and coffee grounds. For a list of permitted and unsuitable items, go to the manufacturer’s guidelines if you’re using a solar compost machine.
7. Harvesting and Using the Compost:
Traditional home composting might take several months to a year to mature, depending on the process and environmental factors. When it smells earthy and has a crumbly, dark texture, it’s ready. Take the completed material out of the compost bin or the bottom of the pile in order to harvest the compost. A separate compartment for finished compost may be included in your solar composting machine. This nutrient-rich substance can be used as a potting mix for container plants, as a top fertilizer for lawns, or to improve the soil in your garden. Compost enhances the structure of the soil, holds onto moisture better, and supplies vital nutrients for plant development.
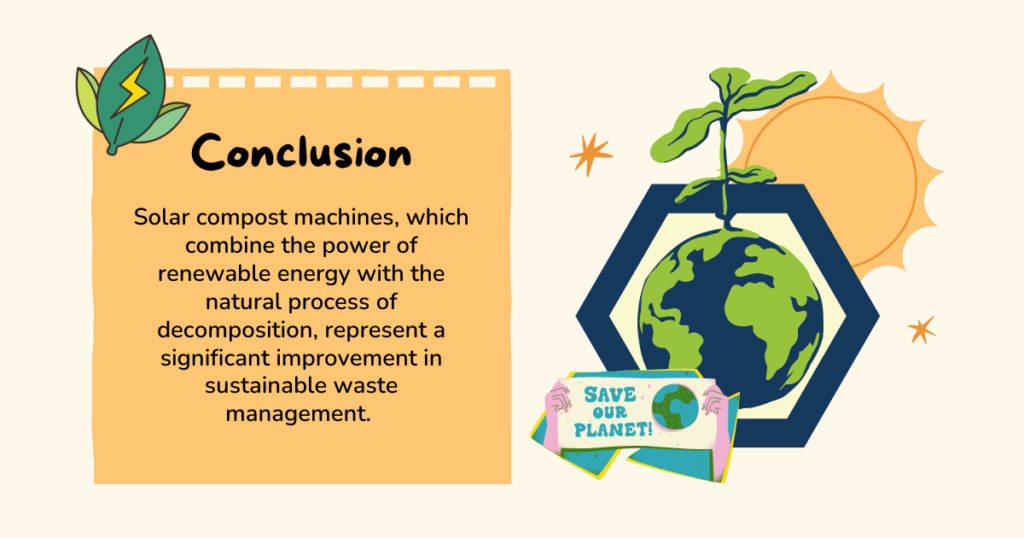
Conclusion:
Solar compost machines, which combine the power of renewable energy with the natural process of decomposition, represent a significant improvement in sustainable waste management. These devices provide communities and households with an eco-friendly and useful answer by effectively turning organic waste into advantageous home compost. The advantages are obvious: less trash, more fertile soil, and a less carbon footprint.
Whether you opt for a high-tech solar compost machine or prefer traditional home composting methods, the practice of composting is a simple yet powerful way to contribute to a healthier environment. By transforming organic waste into rich compost, you not only reduce your environmental impact but also create a valuable resource that can enhance your garden and landscape. Take advantage of solar energy, embrace the green revolution, and set off on a path to a more self-sufficient and sustainable way of living. With a little effort and the right tools, you can turn your kitchen scraps and yard waste into nature’s treasure—black gold for your garden.